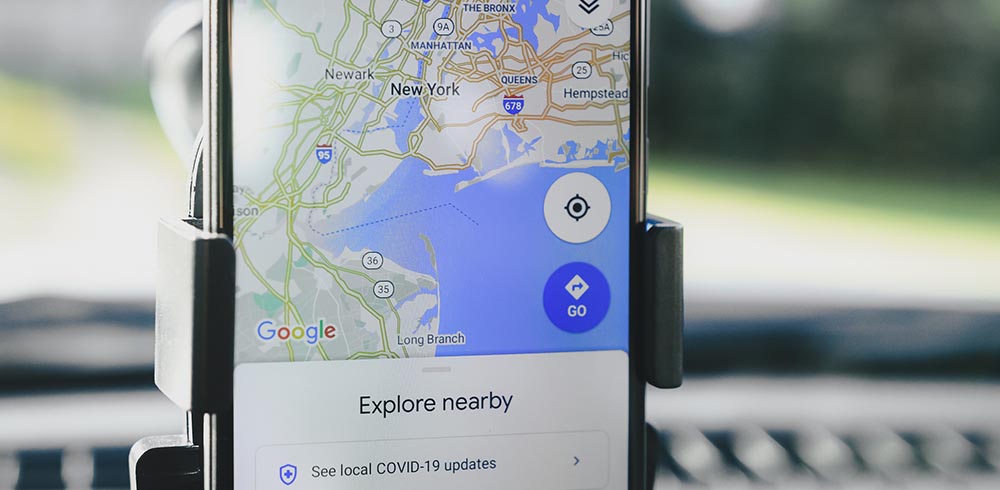
How to avoid accidents with AI on Google Maps?
Google I/O intends to develop a tool integrated into its Google Maps app that would focus on helping to reduce the number of road traffic accidents through Artificial Intelligence (AI).
How will the Google Maps accident-avoidance tool work?
The Google Maps app (either from a mobile phone or integrated into a vehicle’s navigator) will include a function through AI that can detect that a driver brakes the vehicle considerably abruptly and establish a pattern that identifies the speed range of the vehicle, the time and/or the geolocation of the driver to locate possible causes of accidents. Thus, detecting when the car has braked because there was a real danger of a traffic accident.
It is therefore based on analyzing factors such as the time of day, whether there are roadworks or lack of visibility on the routes on which the vehicles are travelling or whether the traffic is busy, in order to determine the dangers and be able to warn users in advance.
This could, for example, detect habitual braking by drivers on a particular route and enable Google Maps to provide users with a safer route.
According to Google Maps, it is estimated that the use of this functionality could prevent up to 100 million accidents occurring due to possible causes that could be analyzed by its AI.
How does the use of this technology affect the processing of personal data?
The use of AI technologies necessarily involves the processing of massive data, including different categories of personal data. AI is an efficient resource for establishing patterns, as well as streamlining processes and operations with massive volumes of information (“Big Data”). However, the problem is that this data processing can lead to biases.
To avoid impartiality in terms of data processing, Google has been perfecting its AI through its “machine learning” models. In short, this is the ability of AI to receive a set of data and learn by itself, changing and adjusting algorithms as it processes information and gains knowledge in relation to the environment.
This machine learning will be developed based on two types of data processed:
- On the one hand, through data from mobile phones and devices that use the Google Maps App.
- On the other, through the data obtained from the geolocation points that any device that has activated the App has passed through. In other words, the routes along which the vehicles have been driven while using Google Maps.
How must this processing be carried out for it to be lawful for Google Maps?
Firstly, the consent of the User is essential when allowing the processing of their personal data by means of the Google Maps tool, either at the time of downloading the app (as this consent must be deactivated by default and must be activated by the user) or if Google Maps is integrated into the vehicle’s GPS navigator, prior to accessing the use of this navigator.
In addition, it is also necessary that the function of the Google Maps tool for the prevention of traffic accidents can be activated and deactivated at the user’s will. In other words, this consent can be revoked at any time.
On the other hand, the purpose of the processing must be solely to identify dangers to be able to subsequently alert users to prevent road accidents. In other words, this data could not, for example, be passed on to insurance companies to be used to personalize accident insurance.
Moreover, the data processing should be carried out in accordance with the principles of:
- Pseudonymization: this consists of processing personal data without the data subject’s identifying data but without removing the link between the data that manages to determine the person holding the data and that Google Maps can subsequently link him or her as a user to whom to offer information to avoid car accidents.
- Minimization: That is, collecting only the personal data to be processed, only at the time it is to be processed and processing it only for the purpose for which it is collected.
In short, it is a geolocation tool that can indirectly identify users. In this regard, it is important that Google Maps, in this case, establishes appropriate safeguards of minimization and proportionality, the least possible impact in relation to the purpose and guarantees of the processing.

Letslaw es una firma de abogados internacionales especializada en el derecho de los negocios.







